Bulging Disk vs. Herniated disk: What’s the difference?
Back pain can be excruciating. If the pain is really bad, you might have a hard time figuring out what exactly is wrong. There are many different causes for back pain. Among the more common ones are a bulging or a herniated disk. The disks are found between the vertebrae in your spine. They basically act as cushions or shock absorbers between the the bones of your spine. They consist of two layers of cartilage, a tougher layer on the outside and a somewhat softer layer on the inside, according to doctors.
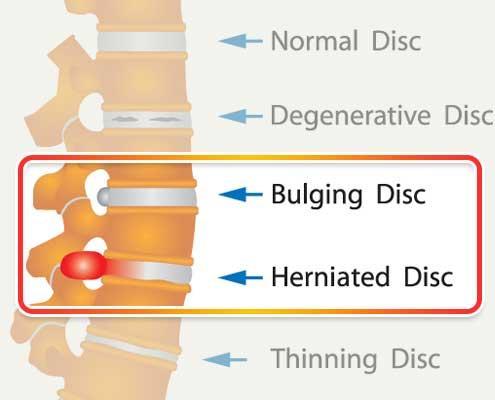
Bulging Disk
The most common cause for a bulging disk is age. Doctors found that the condition can happen to people in their 20’s , but it is more commonly found in people who are in their 30’s and 40’s. When you get older the cartilage could dry out or stiffen and a part of the outer layer of your disk will starts to bulge out. If the bulging disk comes in contact with the spinal nerve, the condition can cause discomfort and pain.
Herniated Disk
A herniated disk means that the outer layer of the disk gets ruptured or cracked and the inner and softer part gets, so-to speak, squeezed out. A herniated disk is likely to cause more pain since it usually extends further out and therefore is more likely to irritate nerve roots. Symptoms of a herniated disk include back pain, numbness or weakness in an arm or a leg. If you feel any back pain visit a specialist.
Louisiana Pain Specialists
- At Louisiana Pain Specialists, our focus is on improving the quality of life of our patients.
- We have helped thousands of our patients get back to doing what is important to them:
working, having restful sleep, spending quality time with friends and family, and participating in their normal daily life. - We have been successful in caring for patients with challenging conditions, for whom other treatment plans have failed.