Facts about Prolapsed Disc
- Prolapsed discs are the most common cause of trips to the ER each year by those experiencing back pain.
- While prolapsed discs occur with age, trauma to the back can also cause this condition to occur, as can certain medical conditions.
- A prolapsed disc is the most common cause of sciatica pain.
Prolapsed Disc Causes and Symptoms
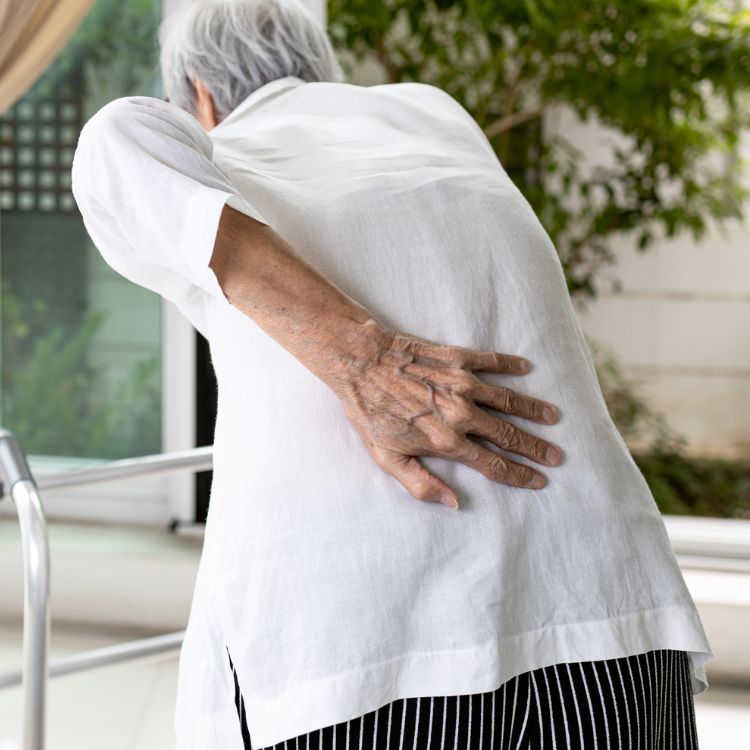
This type of condition can cause pain that occurs within the sciatica, which is a longest nerve within the human body. When pain occurs within the sciatica, it can lead to pain that extends from the upper back, runs through the lower back, and then makes its way through the buttock and thighs. The pain that occurs can also make its way into the feet, and cause pain that is experienced as; numb, aching, burning and tingling.
Causes
Aging of the discs that causes degeneration to occur is the most common cause of this condition. Overtime, the liquid within the discs begins to lessen, and it results in thinning of the jelly substance. While age is the most common factor, those who work in careers that require a lot of manual labor are more prone to getting this disorder. Also, injury to the region can cause a prolapsed disc, and it is seen in those who participate in high impact sports, along with injuries due to falls or other similar accidents.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Prolapsed Discs
When this condition is suspected, your doctor will first do a physical, which is done by applying pressure, and examining the area for signs of irritation. If a prolapsed disc is suspected, the physician will then use imaging devices to determine if the pain is actually caused from the disc. The imaging device used for a disc issue is an x-ray, as this allows the disc to show any problems on the imaging, which will not be shown with other imaging tests, such as an MRI.
Treatment
The most common treatment is physical therapy, as this can often allow the disc to heal on its own. Along with physical therapy, and at home application of compression in hot and cold forms, the disc will generally heal on its own. However, the physician will monitor the condition and see if it’s gets worse or better overtime. If there isn’t any progression in the healing process, surgery may be used to correct the issue. The most common surgery is the use of a non-invasive method which involves making a small incision, and then moving the disc back into its original location. This surgery is typically effective if the disc hasn’t degenerated at a progressive level, and a special bonding material is used to hold the disc in place.