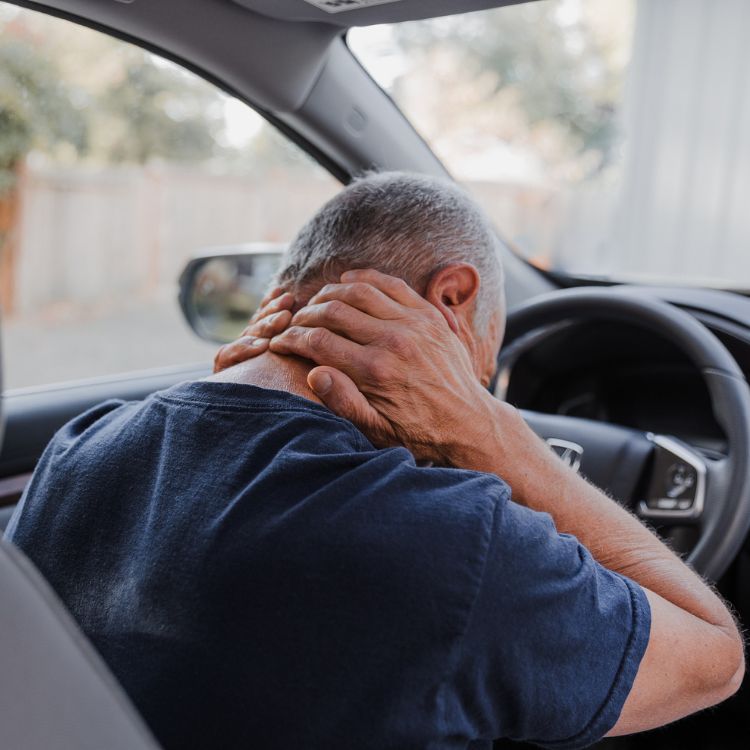
Causes of Whiplash
- Car accidents: Rear-end collisions are the most common cause of whiplash, though any type of car accident can lead to this injury.
- Falls: A sudden fall, especially one where the person lands on their back or head, can result in whiplash-like injuries.
- Sports injuries: Activities such as football, hockey, or other high-impact sports can cause the rapid jerking motion that leads to whiplash.
Symptoms of Whiplash
Symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the injury and may not appear immediately. Common signs include:
- Neck pain and stiffness
- Headaches (often starting at the base of the skull)
- Dizziness
- Shoulder or upper back pain
- Numbness or tingling in the arms
- Reduced range of motion in the neck
- Fatigue
In some cases, more severe symptoms can develop, such as difficulty concentrating, blurred vision, or memory problems. These are known as whiplash-associated disorders and may require more intensive treatment.
Treatment Options for Whiplash
Treatment for whiplash typically involves a combination of rest, pain management, and physical therapy. Some common treatment options include:
- Pain medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Specialized exercises and stretches can help restore range of motion and strengthen the muscles in the neck.
- Ice and heat therapy: Applying ice to the neck in the initial days after injury can reduce swelling, followed by heat to relax tight muscles.
- Chiropractic care or spinal manipulation: This may help realign the neck and improve mobility.
- Cervical collar: A soft cervical collar may be used to provide temporary support and limit neck movement.
In some cases, more advanced treatments, such as injections or surgery, may be considered if symptoms persist despite conservative care.