Injuries
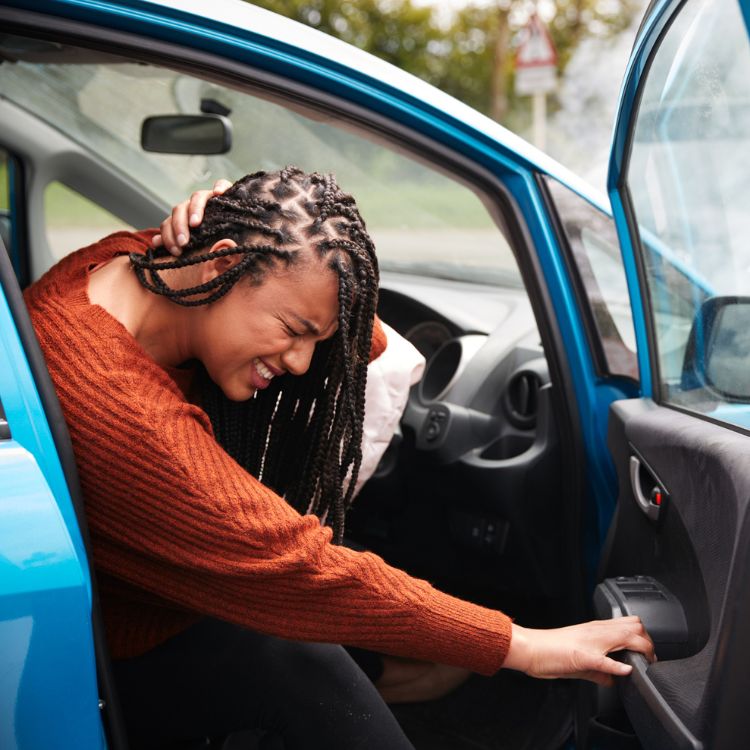
Of all the injuries associated with motor vehicle accidents, chronic whiplash-associated disorder (WAD) represents the most common medical and psycho-social problem. Typically, whiplash presents with mild neck stiffness and soreness. Patients can also have an associated post-traumatic stress disorder. In 2005, physicians studied if the acute stress reaction following a whiplash injury predicted long-term consequences.
Their results demonstrate that both physical and psychological factors play a role in recovery or non-recovery from whiplash injury. This may assist in the development of more relevant treatment methods for acute whiplash (Sterling 2005).
When traveling at a high speed, your body suddenly stops during a car collision. This produces a significant amount of stress on one’s body. Most often, neck muscle and soft tissue straining occurs. In other cases, other injuries may occur including bone fractures, ligament tears, head injuries, internal bleeding, abrasions, and spinal cord injury.
Basic Whiplash Symptoms
If you are experiencing any or all of the following symptoms then you are most likely experiencing whiplash-associated disorder:
- Neck pain
- Headache
- Shoulder pain
- Low back pain
- Difficulty swallowing
- Blurred vision
- Ringing ears
- Nausea
- Fatigue or weakness
- Irritability
- Dizziness
- Vertigo
Treatments for Motor Vehicle Injuries
Following a motor vehicle collision, 15% to 40% of patients who have acute neck pain will eventually develop chronic neck pain (Schofferman 2007). Therefore, it is important to treat the symptoms of whiplash to decrease the chance of developing chronic sequelae. There are many treatments that may be effective for whiplash. NSAIDs reduce the inflammation that forms acutely. Chiropractic manipulations and acupuncture may also help relieve the discomfort.
When the neck pain persists, medial branch blocks of the facet joint can be done to determine whether the facet joints are the cause of pain. When significant relief occurs on two occasions, radiofrequency ablation typically provides significant relief for an estimated eight to 12 months and can be repeated as needed (Scofferman 2007). Botox (botulinum toxin A) injections have recently been studied and show effectiveness in reducing pain and increasing range of motion in patients suffering from whiplash (Juan 2004).